Jacarana Data Access Models
Overview
This document outlines the design of the Jacarana Data Access Models for a Node.js backend system, focusing on the interaction between connectors, entity models, database models, and business logic classes. The architecture ensures a clean, extensible, and maintainable codebase, leveraging modern JavaScript features like async/await and Proxies.
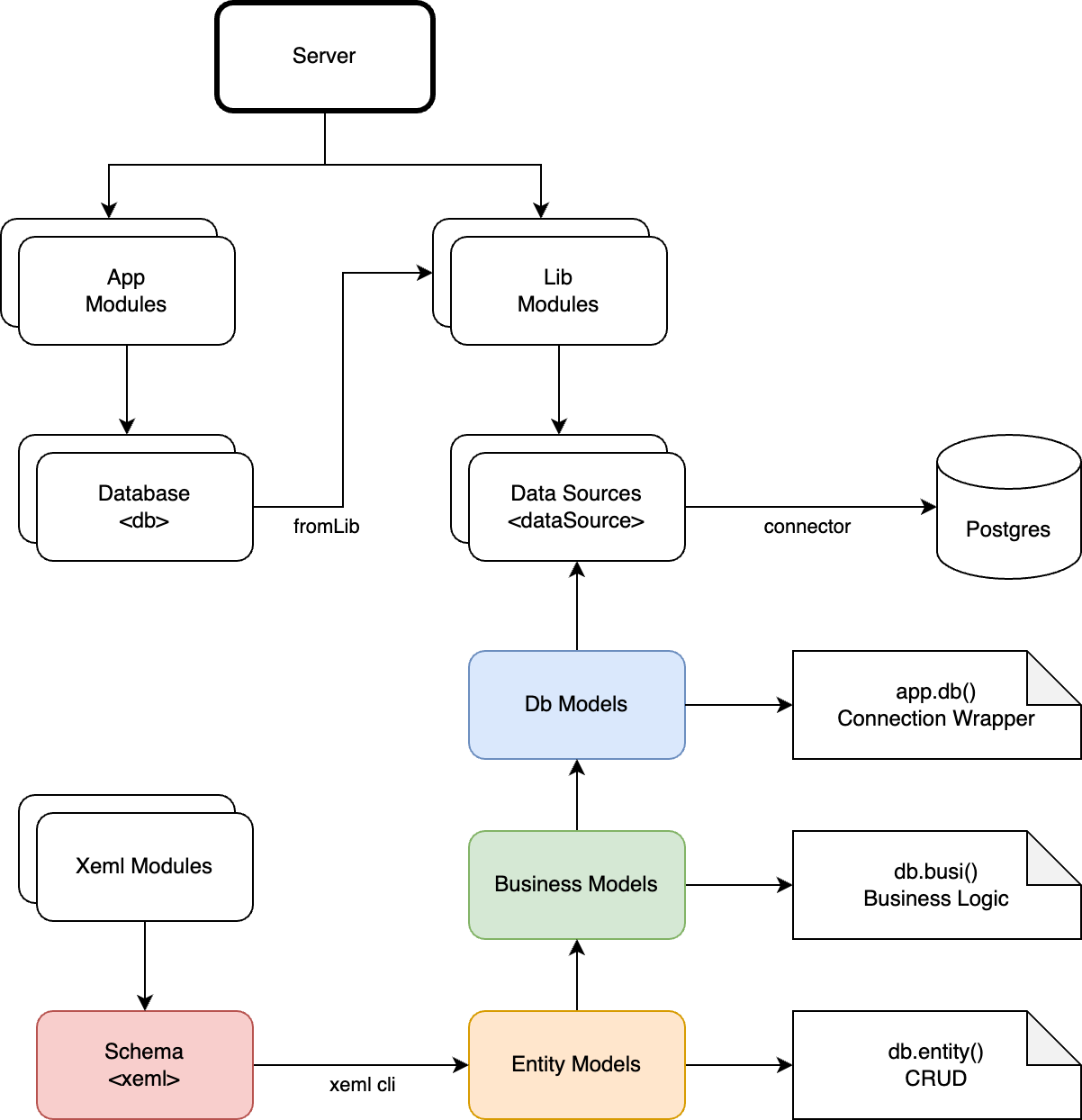
Base Components
- Connector: Manages database connections and connection pools.
- DbModel: Base class for database interactions, managing connections and transactions.
- EntityModel: Base class for ORM entities, encapsulates data through a proxy.
- BusinessLogic: Encapsulates the business logic of the system, interacting with one or more EntityModels and managing transactions.
Specific database features can be implemented in subclasses inheriting from the above base components.
E.g.
- PostgresConnector: Leverages
pgpackage to manage connections and connection pools to PostgreSQL database. - PostgresEntityModel: Supports special query syntax of PostgreSQL, e.g.,
ANY,ALL. - PostgresDbModel: Supports multiple schemas inside a database.
Connector
The Connector class is responsible for managing connections to the database.
Interface
class Connector {
async connect_(); // Get a connection from the pool or create a new one, depending on the driver
async disconnect_(); // Release the connection back to the pool or close it
async end_(); // Close all connections in the pool
async ping_(); // Ping the database
async execute_(); // Execute a query
async beginTransaction_(); // Begin a transaction
async commit_(); // Commit a transaction
async rollback_(); // Rollback a transaction
async create_(model, data, options, connection) -> ({ data, affectedRows })
async find_(model, options, connection) -> ({ data })
async update_(model, data, options, connection) -> ({ data, affectedRows })
async delete_(model, options, connection) -> ({ data, affectedRows })
async upsert_(model, data, uniqueKeys, dataOnInsert, options, connection) -> ({ data, affectedRows })
}
EntityModel
The EntityModel class serves as a base class for data entities with static meta providing metadata. EntityModel instance itself does not save any data since JS always handles data in the form of JSON and it's not necessary to implement an ActiveRecord-like class.
Interface
class EntityModel {
get meta(); // Entity metadata, { name, keyField, associations, features }
async findOne_(criteria); // Implement find one logic
async findMany_(criteria); // Implement find many logic
async findAll_(); // Implement find all logic
async createOne_(data); // Implement create one logic
async createMany_(dataArray); // Implement create many logic
async updateOne_(criteria, data); // Implement update one logic
async deleteOne_(criteria); // Implement delete one logic
}
DbModel
The DbModel class manages the lifecycle of a connection created from the connector, and all EntityModel instances are created from DbModel. DbModel uses Proxy to delegate PascalCase getter to the entity(getterName) method.
Interface
class DbModel {
get meta(); // Database metadata, { schemaName, Entities }
entity(name); // Get an entity instance
async transaction_(async function(anotherDbInstance));
}
BusinessLogic
The BusinessLogic class encapsulates the business logic of the system. It interacts with one or more EntityModel instances and manages transactions to complete a business operation.
Interface
class BusinessLogic {
constructor(db) {
this.db = db;
}
async validateUserPassword(username, password) {
// Example business operation logic
await this.db.transaction_(async (db) => { // !! the passed in db instance is different with this.db
const user = await db.entity('User').findOne_({ username });
// verify user password with hashed password
});
}
// Other business logic methods
}
Usage
- A default
DbModelinstancedbcan be retrieved from the Jacarana App instance.
const db = app.db('db name');
const businessLogic = new BusinessLogic(db);
- For a normal query
const User = db.entity('User');
const user = await User.findOne_({ id: 1837 });
Summary
This architecture provides a robust and flexible foundation for database access and management, supporting multiple database types and schemas, and enabling seamless integration of data operations with transaction management. The introduction of the BusinessLogic layer ensures that business operations are encapsulated, maintainable, and scalable. The use of async interfaces and proxies ensures modern, efficient, and maintainable code.